Price Floors And Price Ceilings Quizlet

A price floor example.
Price floors and price ceilings quizlet. But this is a control or limit on how low a price can be charged for any commodity. They each have reasons for using them but there are large efficiency losses with both of them. Surplus of 20 units. Price floors and price ceilings.
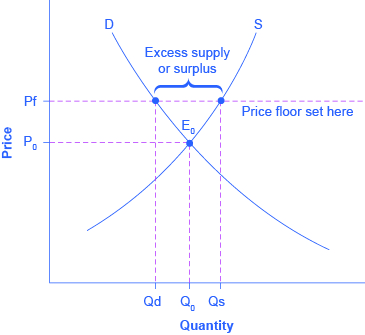
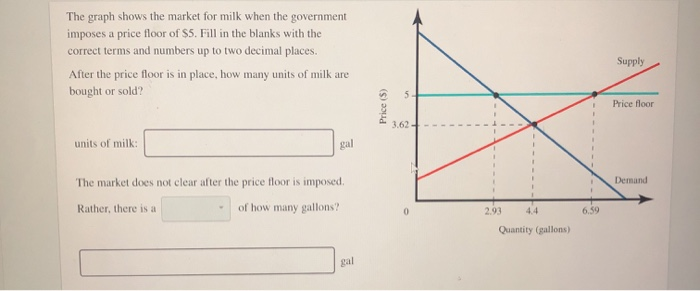
Quantity supplied at the price floor exceeds the amount at the equilibrium price and quantity demanded is less than the amount at the equilibrium price. Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools. Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools. Surplus of 40 units.
Shortage of 0 units. The effect of government interventions on surplus. In the 1970s the u s. Start studying economics 4.
Quantity demanded at the price ceiling exceeds the amount at the equilibrium price and quantity supplied is less than the amount at the equilibrium price. Example breaking down tax incidence. Start studying price ceilings and floors. The opposite of a price ceiling is a price floor which sets a minimum price at which a product or service can be sold.
Shortage of 50 units. Real life example of a price ceiling. If a price ceiling were set at 12 there would be a. The result of a binding price floor is.
Like price ceiling price floor is also a measure of price control imposed by the government. It is legal minimum price set by the government on particular goods and services in order to prevent producers from being paid very less price. Price ceilings and price floors. Price floors and price ceilings are price controls examples of government intervention in the free market which changes the market equilibrium.
The intersection of demand d and supply s would be at the equilibrium point e 0. This is the currently selected item. Taxes and perfectly inelastic demand. Taxation and dead weight loss.
Percentage tax on hamburgers. Price and quantity controls. Final exam ch.